Imagine this: you wake up feeling under the weather. Instead of dragging yourself to the doctor’s office, you open an app on your phone. It asks you questions about your symptoms, analyzes your voice and facial expressions, and even checks your vitals using a connected device. Moments later, the app tells you it suspects the flu and recommends medication and home remedies.
This scenario, once science fiction, is becoming increasingly possible with the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare. But can AI truly replace your doctor? The answer, like most things in medicine, is complex.
Let’s delve into the world of AI in healthcare and explore its potential to transform how we receive care. We’ll also examine the limitations of AI and why human doctors are likely to remain essential for a healthy future.
AI’s Superpowers in Healthcare
AI is a branch of computer science that allows machines to learn and mimic human intelligence. In healthcare, AI is being harnessed for a variety of purposes, including:
Diagnosis
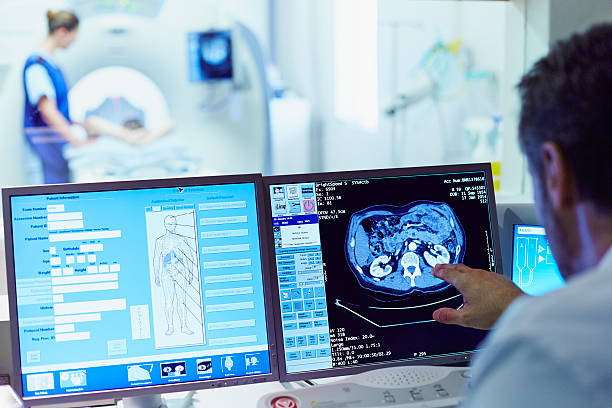
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, imaging scans, and lab results. This allows them to identify patterns that doctors might miss and suggest potential diagnoses with greater accuracy. For instance, in radiology, AI can enhance image interpretation, detecting abnormalities in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with remarkable precision. Studies have shown that AI systems can match or even exceed human experts in identifying conditions such as fractures, tumors, and lung diseases. Moreover, AI-driven diagnostic tools can integrate data from various sources, offering a comprehensive view that supports early detection of diseases, leading to better outcomes.
Treatment Planning
AI can help doctors create personalized treatment plans by considering a patient’s unique medical history, genetic makeup, and response to past treatments. This can lead to more effective and targeted therapies. For example, in oncology, AI algorithms can analyze genetic information to identify mutations driving cancer growth, enabling the selection of targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective. Additionally, AI can predict a patient’s response to certain treatments based on historical data, potentially avoiding ineffective therapies and minimizing side effects. In chronic disease management, AI can continuously monitor patient data, adjusting treatment plans in real-time to improve disease control and patient quality of life.
Drug Discovery
AI can analyze large datasets of molecular structures to accelerate the development of new drugs and therapies. Traditional drug discovery processes are time-consuming and costly, often taking over a decade and billions of dollars to bring a new drug to market. AI can significantly shorten this timeline by predicting how different molecules will interact with biological targets, identifying promising compounds early in the research process. Machine learning models can sift through vast chemical libraries, proposing candidates for synthesis and testing. Additionally, AI can repurpose existing drugs by finding new therapeutic uses for them, potentially bringing effective treatments to patients more quickly.
Surgery and Robotics
AI-powered surgical robots can assist surgeons with delicate procedures, improving precision and minimizing complications. These robots can perform tasks such as suturing, tissue manipulation, and navigation in complex anatomical landscapes with a level of accuracy and steadiness that surpasses human capabilities. For example, robotic systems like the da Vinci Surgical System provide enhanced visualization and dexterity, enabling minimally invasive procedures that reduce patient recovery times and postoperative pain. AI algorithms also assist in preoperative planning by simulating surgeries and predicting potential challenges, allowing surgeons to strategize and optimize their approach.
Administrative Tasks
AI can handle tedious administrative tasks such as scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and processing insurance claims, freeing up doctors’ time to focus on patient care. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms can transcribe and organize clinical notes, ensuring accurate and up-to-date patient records. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can interact with patients to schedule appointments, provide reminders, and answer basic inquiries, enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction. In the realm of insurance, AI can automate the verification and approval of claims, reducing administrative burden and expediting the reimbursement process. These efficiencies not only improve the workflow but also reduce operational costs for healthcare providers.
These are just a few examples, and the potential applications of AI in healthcare are constantly evolving.
AI: Not Quite Human, But a Powerful Ally
While AI is revolutionizing healthcare, it’s important to remember it’s not a human doctor. AI excels at analyzing data and identifying patterns, but it lacks crucial human qualities like empathy, intuition, and the ability to build rapport with patients.
Here are some key limitations of AI in healthcare:
Limited Understanding of Context:
AI algorithms rely on data, and they may not always understand the nuances of a patient’s situation. A cough could be a sign of a cold, or it could be a symptom of something more serious. A human doctor can consider a patient’s medical history, lifestyle factors, and emotional state to make a more informed diagnosis.
Ethical Concerns:
AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on. Biases in the data can lead to biased algorithms, which could disadvantage certain groups of patients. Additionally, there are ethical concerns around who has access to patient data and how it’s used.
The Human Touch Matters:
Going to the doctor isn’t just about getting a diagnosis or a prescription. It’s also about building trust, receiving emotional support, and feeling heard. AI can’t replicate the human connection that’s essential for good healthcare.
The Doctor-AI Partnership:
The Future of Care The most likely scenario isn’t AI replacing doctors, but rather AI working alongside doctors to improve patient care. Imagine a future where AI acts as a powerful assistant, analyzing data, suggesting diagnoses, and even providing preliminary treatment plans. This would free up doctors’ time to focus on what they do best – interacting with patients, providing emotional support, and making complex medical decisions.
Here are some potential benefits of the doctor-AI partnership:
Improved Diagnoses
AI can assist doctors in catching potential diagnoses that may be missed otherwise. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that might be overlooked in manual reviews. For instance, AI systems in radiology can detect minute changes in imaging scans, suggesting possible conditions like early-stage cancer, small fractures, or subtle cardiovascular issues. These insights enable doctors to make more accurate diagnoses, reduce the likelihood of misdiagnosis, and ensure that patients receive appropriate treatment sooner.
More Personalized Care
AI can help doctors tailor treatment plans to each patient’s individual needs. By integrating data from electronic health records, genetic profiles, and past treatment outcomes, AI can suggest personalized therapeutic strategies. For example, in oncology, AI can recommend specific chemotherapy regimens based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup and the molecular characteristics of their tumor. This approach increases the likelihood of treatment success and minimizes adverse effects. In managing chronic diseases like diabetes or hypertension, AI can customize lifestyle and medication recommendations, improving patient adherence and health outcomes.
Increased Efficiency
AI can handle administrative tasks, allowing doctors to spend more time with patients. Tasks such as appointment scheduling, patient record management, and insurance claim processing can be automated with AI. This reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers and streamlines operations. For example, AI-powered systems can automatically update patient records after each visit, ensuring accurate and comprehensive documentation. Virtual assistants and chatbots can manage appointment bookings and follow-ups, reducing wait times and enhancing patient satisfaction. As a result, doctors can focus more on direct patient care, improving the overall quality of service.
Earlier Detection of Disease
AI can analyze data like wearable device readings to identify potential health problems at an earlier stage. Wearable devices and health apps generate continuous streams of data, including heart rate, physical activity, sleep patterns, and other vital signs. AI algorithms can monitor these metrics in real-time, alerting healthcare providers to early signs of disease or deviations from normal patterns. For instance, AI can detect irregular heart rhythms that may indicate atrial fibrillation or predict exacerbations in chronic conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) before they become critical. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve long-term health outcomes.
Greater Accessibility to Care
AI-powered telehealth services can provide access to care in underserved areas. Telehealth platforms equipped with AI can offer remote consultations, diagnostic support, and patient monitoring, making healthcare more accessible to individuals in rural or remote locations. AI can assist in triaging patients, determining the urgency of their conditions, and directing them to appropriate care levels. Additionally, AI-driven diagnostic tools can empower healthcare providers in resource-limited settings to make informed decisions without the need for specialized equipment or personnel. This democratization of healthcare technology ensures that more people receive timely and adequate care, reducing disparities in health access and outcomes.
The Road Ahead: Preparing for the AI-Powered Healthcare Landscape
The rise of AI in healthcare presents both challenges and opportunities. To ensure AI benefits patients and doctors alike, it’s crucial to address the limitations and ethical concerns surrounding this technology. Here are some steps that can be taken:
Developing Transparent and Explainable AI
AI algorithms should be designed in a way that allows doctors to understand how they reached a particular diagnosis or recommendation. Transparency in AI systems means that the decision-making processes are open and understandable to users. Explainable AI (XAI) involves creating models that provide insights into how decisions are made, which can help in gaining trust from healthcare providers and patients. This transparency is critical, as it allows clinicians to validate AI recommendations and integrate them into their practice confidently. Techniques like interpretable models, visualizations, and decision trees can help make AI outputs more understandable.
Addressing Bias in AI
We need to ensure that AI datasets are diverse and representative of the population to avoid biased algorithms. Bias in AI can lead to unfair treatment of certain patient groups, resulting in disparities in healthcare outcomes. To address this, it is essential to use diverse datasets during the training phase, ensuring that the data reflects various demographics, including different ages, genders, ethnicities, and socioeconomic backgrounds. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and evaluation of AI systems are necessary to identify and mitigate any biases that may emerge over time. Implementing fairness-aware algorithms and conducting bias audits can help create more equitable AI applications.
Prioritizing Data Privacy and Security
Strong data protection measures are essential to ensure patient privacy and security in the age of AI-powered healthcare. Healthcare data is highly sensitive, and its protection is paramount. Robust cybersecurity protocols, encryption techniques, and secure data storage solutions are necessary to protect patient information from unauthorized access and breaches. Compliance with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe is crucial. Ensuring that AI systems adhere to these standards can help maintain trust and safeguard patient privacy.
Investing in AI Education for Healthcare Professionals
Doctors and nurses need training to understand how to work effectively with AI tools and interpret their outputs. Comprehensive education and training programs should be developed to familiarize healthcare professionals with AI technologies. This includes understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI, interpreting AI-generated insights, and integrating these tools into clinical workflows. Continuous professional development opportunities, such as workshops, online courses, and certifications in AI and data science, can help bridge the knowledge gap and empower healthcare providers to leverage AI effectively.
Ensuring Equitable Access to AI Technology
We need to bridge the digital divide to ensure everyone has access to the benefits of AI-powered healthcare. Equitable access involves providing the necessary infrastructure, resources, and support to underserved and rural communities. This includes investing in high-speed internet, affordable AI-enabled devices, and telehealth services.
Policymakers and healthcare organizations must work together to develop strategies that promote inclusivity and address barriers to access. Grants, subsidies, and public-private partnerships can play a significant role in making AI-powered healthcare accessible to all, regardless of geographical location or socioeconomic status.
By taking these steps, the healthcare industry can harness the full potential of AI, ensuring that it serves as a valuable tool in improving patient outcomes, enhancing the efficiency of care delivery, and promoting health equity.
Beyond the Hype: A Human-Centric Approach to Healthcare with AI
It’s important to remember that AI is a tool, not a replacement for human doctors. The future of healthcare lies in a collaborative approach where AI empowers doctors to deliver better care. Here are some key considerations for a human-centric healthcare future with AI:
Maintaining the Doctor-Patient Relationship:
The doctor-patient relationship will remain central to good healthcare. AI should enhance, not replace, the trust and communication between doctors and patients.
Focus on Empathy and Communication:
Medical schools and healthcare institutions should continue to emphasize the importance of empathy, communication skills, and bedside manner in training future doctors.
Empowering Patients with Information:
Patients should be empowered to understand how AI is used in their care and have a say in how their data is used.
By addressing these challenges and prioritizing human-centered care, we can harness the power of AI to create a future where healthcare is more accurate, efficient, and accessible for everyone.
This future holds immense potential. Imagine a world where AI helps doctors diagnose diseases earlier, develop personalized treatment plans, and even predict potential health risks before they develop. This could lead to better health outcomes, improved quality of life, and a future where preventive care takes center stage.
However, it’s crucial to remember that AI is a tool, and like any tool, it can be misused. We must ensure that AI is developed and used responsibly, with the ethical considerations and human element remaining paramount.
The future of healthcare with AI is bright, but it’s a future we need to shape together. By working collaboratively, doctors, patients, and AI developers can build a healthcare system that leverages technology to improve the lives of everyone.